
下载APP

【简答题】


Exercise I. Directions: Complete the following sentences with the appropriate forms of the words in brackets. 1) Please try to be more and help us when you are asked. (cooperate) 2) He made a polite that he was going to leave. (imply) 3) Paul is amazingly in trying to get Gina to go out with him. (persist) 4) It’s a(n) sort of a house with books and papers lying around everywhere. (order) 5) He finally found a job as a (n) in a joint venture ( 合资企业 ). (account) 6) No one has yet come up with a satisfactory of terrorism. (define) 7) This problem should be discussed first, as it takes over all the others. (precede) 8) Mr Brown is a(n) pianist, and gives concerts all over the world. (accomplish) 9) Young people were in the at this meeting. (major) 10) Are your opinions of the views of all the students? (represent) Exercise II. Directions: Fill in the blanks with appropriate prepositions or adverbs. 11) The bullet struck his head and he was killed the spot. 12) They are saving for their wedding next year. 13) Don’t worry, we have plenty of time to talk it . 14) She has a real aptitude singing and dancing. 15) Only 3% of the blacks were registered voters 97% of the white residents. 16) He studied the contract detail before signing it. 17) He is seen the most promising tennis player in the university. 18) Nobody knows when the universe came being. 19) She volunteered the job as coordinator of the fund –raising campaign. 20) The UN negotiators have worked a set of compromise proposals.
题目标签:合资企业
举报
参考答案:


参考解析:




刷刷题刷刷变学霸
举一反三

【单选题】"We thought there was a future in nuclear power when no one else believed in it," says Anne Lauvergeon, chief executive of Areva. The French, government-owned company is building the first nuclear rea...
A.
The French company -- Areva’s monopoly status in nuclear market.
B.
People’s ever pessimistic view on nuclear power.
C.
The high cost of nuclear plants and the indefinite cost of nuclear energy.
D.
Governments’ concentration on solving climate problems.
【单选题】"We thought there was a future in nuclear power when no one else believed in it," says Anne Lauvergeon, chief executive of Areva. The French, government-owned company is building the first nuclear rea...
A.
Areva’s capacity is much bigger than Westinghouse and GE Hitachi
B.
readers figures to attract their attention
C.
readers the existing truth in nuclear market
D.
nuclear power has been in the state of revival
【单选题】Passage Two "We thought there was a future in nuclear power when no one else believed in it," says Anne Lauvergeon, chief executive of Areva. The French, government-owned company is buil...
A.
It is a French company, used to be owned by. private sector.
B.
It has stepped into the third-generation .reactor design period.
C.
Its third generation reactor has been constructed in France, Finland and China.
D.
Its nuclear capacity will occupy one-third of the total in less than a decade.
【单选题】"We thought there was a future in nuclear power when no one else believed in it," says Anne Lauvergeon, chief executive of Areva. The French, government-owned company is building the first nuclear rea...
A.
With hardly any other resource, they chose nuclear as a way.
B.
They have always been sticking to building new reactors.
C.
They construct nuclear reactors only for their own use.
D.
Nicolas Sarkozy toured to promote nuclear expertise to win election.
【单选题】"We thought there was a future in nuclear power when no one else believed in it," says Anne Lauvergeon, chief executive of Areva. The French, government-owned company is building the first nuclear rea...
A.
Areva’s EPRs are under construction at Flamanville in Normandy, Olkiluoto in Finland and Taishan in China. Areva forecasts that demand for nuclear capacity could bring it orders for 60 reactors, or one-third of the total market, by 2020 -- each with a price of around 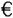 5 billion. Westinghouse has orders from China for four of its new AP1000 reactors, and GE Hitachi’s ESBWR design is being considered by several American utilities.The high cost of building new plants, arid the uncertainty over the cost of nuclear energy relative to other sources, could delay the nuclear renaissance (复兴), especially in the midst of a credit crunch. Luckily for sellers, governments are bent on tackling climate change and securing energy supplies, and are likely to offer big subsidies.Britain, for one, has given its blessing to France’s nuclear ambitions: in September Electricit6 de France (EDF), a state-owned energy giant which owns and runs France’s plants (and is thus closely intertwined with Areva), bought British Energy, a troubled utility in which the British government held a big share.
5 billion. Westinghouse has orders from China for four of its new AP1000 reactors, and GE Hitachi’s ESBWR design is being considered by several American utilities.The high cost of building new plants, arid the uncertainty over the cost of nuclear energy relative to other sources, could delay the nuclear renaissance (复兴), especially in the midst of a credit crunch. Luckily for sellers, governments are bent on tackling climate change and securing energy supplies, and are likely to offer big subsidies.Britain, for one, has given its blessing to France’s nuclear ambitions: in September Electricit6 de France (EDF), a state-owned energy giant which owns and runs France’s plants (and is thus closely intertwined with Areva), bought British Energy, a troubled utility in which the British government held a big share.
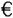 5 billion. Westinghouse has orders from China for four of its new AP1000 reactors, and GE Hitachi’s ESBWR design is being considered by several American utilities.The high cost of building new plants, arid the uncertainty over the cost of nuclear energy relative to other sources, could delay the nuclear renaissance (复兴), especially in the midst of a credit crunch. Luckily for sellers, governments are bent on tackling climate change and securing energy supplies, and are likely to offer big subsidies.Britain, for one, has given its blessing to France’s nuclear ambitions: in September Electricit6 de France (EDF), a state-owned energy giant which owns and runs France’s plants (and is thus closely intertwined with Areva), bought British Energy, a troubled utility in which the British government held a big share.
5 billion. Westinghouse has orders from China for four of its new AP1000 reactors, and GE Hitachi’s ESBWR design is being considered by several American utilities.The high cost of building new plants, arid the uncertainty over the cost of nuclear energy relative to other sources, could delay the nuclear renaissance (复兴), especially in the midst of a credit crunch. Luckily for sellers, governments are bent on tackling climate change and securing energy supplies, and are likely to offer big subsidies.Britain, for one, has given its blessing to France’s nuclear ambitions: in September Electricit6 de France (EDF), a state-owned energy giant which owns and runs France’s plants (and is thus closely intertwined with Areva), bought British Energy, a troubled utility in which the British government held a big share.【单选题】Passage Two "We thought there was a future in nuclear power when no one else believed in it," says Anne Lauvergeon, chief executive of Areva. The French, government-owned company is buil...
A.
Areva’s capacity is much bigger than Westinghouse and GE Hitachi
B.
readers figures to attract their attention
C.
readers the existing truth in nuclear market
D.
nuclear power has been in the state of revival
【单选题】合资企业的定义是()。
A.
两个企业基于营利的需要合并为一个组织
B.
两个人组建合作制企业,分担工作并分享利润
C.
两个组织为营利投入资金和专门技术组建一个新组织
D.
为了确保营利政府部门对私人企业的接管
相关题目:

【单选题】"We thought there was a future in nuclear power when no one else believed in it," says Anne Lauvergeon, chief executive of Areva. The French, government-owned company is building the first nuclear rea...
A.
The French company -- Areva’s monopoly status in nuclear market.
B.
People’s ever pessimistic view on nuclear power.
C.
The high cost of nuclear plants and the indefinite cost of nuclear energy.
D.
Governments’ concentration on solving climate problems.
【单选题】"We thought there was a future in nuclear power when no one else believed in it," says Anne Lauvergeon, chief executive of Areva. The French, government-owned company is building the first nuclear rea...
A.
Areva’s capacity is much bigger than Westinghouse and GE Hitachi
B.
readers figures to attract their attention
C.
readers the existing truth in nuclear market
D.
nuclear power has been in the state of revival
【单选题】Passage Two "We thought there was a future in nuclear power when no one else believed in it," says Anne Lauvergeon, chief executive of Areva. The French, government-owned company is buil...
A.
It is a French company, used to be owned by. private sector.
B.
It has stepped into the third-generation .reactor design period.
C.
Its third generation reactor has been constructed in France, Finland and China.
D.
Its nuclear capacity will occupy one-third of the total in less than a decade.
【单选题】"We thought there was a future in nuclear power when no one else believed in it," says Anne Lauvergeon, chief executive of Areva. The French, government-owned company is building the first nuclear rea...
A.
With hardly any other resource, they chose nuclear as a way.
B.
They have always been sticking to building new reactors.
C.
They construct nuclear reactors only for their own use.
D.
Nicolas Sarkozy toured to promote nuclear expertise to win election.
【单选题】"We thought there was a future in nuclear power when no one else believed in it," says Anne Lauvergeon, chief executive of Areva. The French, government-owned company is building the first nuclear rea...
A.
Areva’s EPRs are under construction at Flamanville in Normandy, Olkiluoto in Finland and Taishan in China. Areva forecasts that demand for nuclear capacity could bring it orders for 60 reactors, or one-third of the total market, by 2020 -- each with a price of around 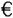 5 billion. Westinghouse has orders from China for four of its new AP1000 reactors, and GE Hitachi’s ESBWR design is being considered by several American utilities.The high cost of building new plants, arid the uncertainty over the cost of nuclear energy relative to other sources, could delay the nuclear renaissance (复兴), especially in the midst of a credit crunch. Luckily for sellers, governments are bent on tackling climate change and securing energy supplies, and are likely to offer big subsidies.Britain, for one, has given its blessing to France’s nuclear ambitions: in September Electricit6 de France (EDF), a state-owned energy giant which owns and runs France’s plants (and is thus closely intertwined with Areva), bought British Energy, a troubled utility in which the British government held a big share.
5 billion. Westinghouse has orders from China for four of its new AP1000 reactors, and GE Hitachi’s ESBWR design is being considered by several American utilities.The high cost of building new plants, arid the uncertainty over the cost of nuclear energy relative to other sources, could delay the nuclear renaissance (复兴), especially in the midst of a credit crunch. Luckily for sellers, governments are bent on tackling climate change and securing energy supplies, and are likely to offer big subsidies.Britain, for one, has given its blessing to France’s nuclear ambitions: in September Electricit6 de France (EDF), a state-owned energy giant which owns and runs France’s plants (and is thus closely intertwined with Areva), bought British Energy, a troubled utility in which the British government held a big share.
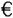 5 billion. Westinghouse has orders from China for four of its new AP1000 reactors, and GE Hitachi’s ESBWR design is being considered by several American utilities.The high cost of building new plants, arid the uncertainty over the cost of nuclear energy relative to other sources, could delay the nuclear renaissance (复兴), especially in the midst of a credit crunch. Luckily for sellers, governments are bent on tackling climate change and securing energy supplies, and are likely to offer big subsidies.Britain, for one, has given its blessing to France’s nuclear ambitions: in September Electricit6 de France (EDF), a state-owned energy giant which owns and runs France’s plants (and is thus closely intertwined with Areva), bought British Energy, a troubled utility in which the British government held a big share.
5 billion. Westinghouse has orders from China for four of its new AP1000 reactors, and GE Hitachi’s ESBWR design is being considered by several American utilities.The high cost of building new plants, arid the uncertainty over the cost of nuclear energy relative to other sources, could delay the nuclear renaissance (复兴), especially in the midst of a credit crunch. Luckily for sellers, governments are bent on tackling climate change and securing energy supplies, and are likely to offer big subsidies.Britain, for one, has given its blessing to France’s nuclear ambitions: in September Electricit6 de France (EDF), a state-owned energy giant which owns and runs France’s plants (and is thus closely intertwined with Areva), bought British Energy, a troubled utility in which the British government held a big share.【单选题】Passage Two "We thought there was a future in nuclear power when no one else believed in it," says Anne Lauvergeon, chief executive of Areva. The French, government-owned company is buil...
A.
Areva’s capacity is much bigger than Westinghouse and GE Hitachi
B.
readers figures to attract their attention
C.
readers the existing truth in nuclear market
D.
nuclear power has been in the state of revival
【单选题】(P150)合资企业的主要方式不包括()
A.
营销合资
B.
合作科研
C.
合作生产原材料和零配件
D.
合作创立新公司
【单选题】合资企业的定义是()。
A.
两个企业基于营利的需要合并为一个组织
B.
两个人组建合作制企业,分担工作并分享利润
C.
两个组织为营利投入资金和专门技术组建一个新组织
D.
为了确保营利政府部门对私人企业的接管
【多选题】国际合资企业的特点有()。
A.
共同投资
B.
共负盈亏
C.
权利相等
D.
财产相同
E.
利益平分

