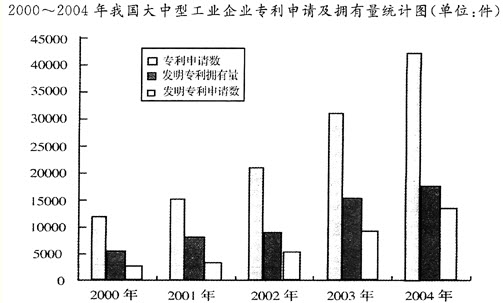
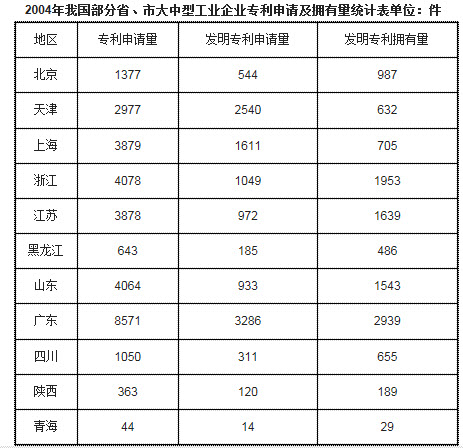
下载APP

【单选题】


What is the passage mainly about?()
A.The Beijing Red Poppy Ladies Percussion.
B.A trend born--the 12 Girls Band.
C.How to succeed in musical world.
D.Bands that don’t have "a thing" are sure to die fast.
A.
Once the 12 Girls Band became popular, similar groups predictably starting popping up. Musicat and Beautiful Youth 18 were formed last year. Both feature now-familiar formulas of attractive young women playing different instruments in songs that combine modem music with classic Chinese tunes. Yet they add to the mix by throwing in song, dance and even acrobatics. In an interview, noted music critic Jin Zhaojun said the girl band phenomenon was not new to China, as similar acts appeared in the 1980s.
B.
However, the undying rule is that to be successful, bands have to have a novel look. "The 12 Girls Band was the first group to give big live shows and show creativity in how they present their performances. The Beijing Red Poppy Ladies Percussion group, formed in 1999, has made a name for itself because they are the only band that exclusively plays drums and percussion instruments. Bands that don’t have ’a thing’ are sure to die fast," Jin said.
举报
参考答案:


参考解析:




刷刷题刷刷变学霸
举一反三

【单选题】当大气压力和风速一定时,被测空气的干湿球温度差直接反映了( )。
A.
空气湿度的大小
B.
空气中水蒸气分压力的大小
C.
同温度下空气的饱和水蒸气压力的大小
D.
湿球温度下饱和水蒸气压力和干球温度下水蒸气分压力之差的大小
【单选题】It is essential for a policeman to be .trained in criminal law(). A.so that he can catch criminals in the streets B.because many of the criminals he has to catch are dangerous C.so that he can justify...
A.
Real policemen hardly recognize any resemblance (类同之处)between their lives and what they see on TV--if they ever get home in time. There are similarities, of course, but the cops(警官) don’t think much of them.
B.
The first difference is that a policeman’s real life revolves round the law. Most of his training is in criminal law. He has to know exactly what actions are crimes and what evidence can be used to prove them in court. He has to know nearly as much law as a professional lawyer, and what is more, he has to apply it on his feet, in the dark and rain, running down an alley after someone he wants to talk to.
C.
Little of his time is spent in chatting to scanty-clad ([穿衣不多的) ladies or in dramatic confrontations with desperate criminals. He will spend most of his working life typing millions of words on thousands of forms about hundreds of sad, unimportant people who are guilt or not--of stupid, petty crimes.
【单选题】The following are the factors of accidents EXCEPT() A、mood B、tiredness C、carelessness D、weather
A.
Accidents was caused; they don’t just happen. The reason may be easy to see: a shelf out of reach, a patch of ice on the road, an overloaded truck. But merely often than not there is a chain of events leading up to the misfortune—frustration, tiredness or just bad temper—that show what the accident really is, a sort of attack on oneself.
B.
Road accidents, for example, happen frequently after a family quarrel, and we all know people who are accidents-prone, so often at odds with themselves and the world that they seem to cause accidents for themselves and others.
C.
By definition, an accident is something you can not predict or avoid, and the idea which used to be current, that the majority of road accidents are caused by a minority of criminally careless drivers, is not supported by insurance statistics. These show that most accidents involve ordinary motorists in a moment of carelessness or thoughtlessness.
D.
It is not always clear, either, what sort of conditions makes people more likely to have an accident. For instance, the law requires all factories to take safety precautions and most companies have safety committees to make sure the regulations are observed, but still, every day in Britain, some fifty thousand men and women are injured from work due to accidents. These accidents are largely the result of human error or misjudgment—noise and fatigue, boredom or worry are possible factors which contribute to this. Doctors who work in factories have found that those who drink too much, usually people who have a high anxiety level, run three times the normal risk of accidents at work.
【单选题】患者16岁,男性,突然血尿,面色苍白,疲倦、精神差,无发热、咳嗽等,患者主诉二天前进食过蚕豆,血液检查:WBC7.3×109/L,Hb78g/L,RBC265×1012,PLT256×109/L,尿液检查,.尿蛋白(+),RBC0~3/HP,WBC0~5/HP。尿隐血试验阳性。此病人最可能的诊断是
A.
剧列运动引起血红蛋白尿
B.
新生儿溶血引起血红蛋白尿
C.
急性尿毒症引起血红蛋白尿
D.
6-磷酸葡萄糖脱氢酶缺陷引起血红蛋白尿
E.
血型不合输血引起血红蛋白尿
【单选题】随着弗洛伊德精神分析理论的出现,人们广泛探求天性,以此来解释行为、思想和情感。和亚当.斯密的假设相类似,弗洛伊德认为:人并不是理性的,而是由本能支配的,因此,通过理解人的种种本性,就可揭开人的心灵的秘密。对这段话的正确理解是( )
A.
弗洛伊德的观点不同于亚当.斯密
B.
弗洛伊德希望通过理解人的本性来揭开心灵的秘密
C.
弗洛伊德的愿望是好的,但他无法揭开人性的秘密
D.
弗洛伊德精神分析理论是用来揭示感性与理性的关系的