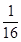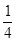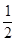下载APP

【单选题】


How Earthquakes Work
An earthquake is one of the most terrifying phenomena that nature can dish up.We generally think of the ground we stand on as 'rock-solid' and completely stable.But an earthquake can shatter that perception instantly.Up until relatively recently, scientists only had unsubstantiated guesses as to what actually caused earthquakes.Even today there is still a certain amount of mystery surrounding them, but scientists have a much clearer understanding.There has been enormous progress in the past century: Scientists have identified the forces that cause earthquakes, and developed technology that can tell us an earthquake's magnitude and origin.The next hurdle is to find a way of predicting earthquakes.
Shaking Ground
An earthquake is a vibration that travels through the earth's crust.Technically, a large truck that rumbles down the street is causing a mini-earthquake, if you feel your house shaking as it goes by, but we tend to think of earthquakes as s that affect a fairly large area, such as an entire city.All kinds of things can cause earthquakes:
-volcanic eruptions
-meteor(流星) impacts
-underground explosions (an underground nuclear test, for example)
-collapsing structures (such as a collapsing mine)
But the majority of naturally-occurring earthquakes are caused by movements of the earth's plates, as we'll see in the next section.
We only hear about earthquakes in the news every once in a while, but they are actually an everyday occurrence on our planet.According to the United States Geological Survey, more than three million earthquakes occur every year.That's about 8000 a day, or one every 11 seconds! The vast majority of these 3 million quakes are extremely weak.
Sliding Plates
The biggest scientific breakthrough in the history of seismology(地震学)—the study of earthquakes came in the middle of the 20th century, with the development of the theory of plate tectonics(板块构造).The basic theory is that the suce layer of the earth—the lithosphere—is comprised of many plates that slide over the lubricating mantle(地幔) layer.At the boundaries between these huge plates of soil and rock, three different things can happen:
-Plates can move apart—If two plates are moving apart from each other, hot, molten rock flows up from the layers of mantle below the lithosphere.
-Plates can push together—If the two plates are moving toward each other, one plate typically pushes under the other one.At some boundaries where two plates meet, neither plate is in a position to subduct under the other, so they both push against each other to form.mountains.
-Plates slide against each other—At other boundaries, plates simply slide by each other—they are pushed tightly together.A great deal of tension builds at the boundary.
Where these plates meet, you'll find faults—breaks in the earth's crust where the blocks of rock on each side are moving in different directions.Earthquakes are much more common along fault lines than they are anywhere else on the planet.
Faults
Scientists identify four types of faults, characterized by the position of the fault plane, the break in the rock and the movement of the two rock blocks:
-In a normal fault (see animation below), the fault plane is nearly vertical.These faults occur where the crust is being pulled apart, due to the pull of a divergent plate boundary.
-The fault plane in a reverse fault is also nearly vertical, but the hanging wall pushes up and the footwall pushes down.This sort of fault forms where a plate is being compressed.
-A thrust fault moves the same way as a reverse fault, but the fault line is nearly horizontal.This is the sort of fault that occurs in a converging plate boundary.
-In
A.
Y
B.
N
C.
NG
举报
参考答案:


参考解析:




刷刷题刷刷变学霸
举一反三

【多选题】建筑幕墙防火构造技术要求有( )。
A.
幕墙与各层楼板之间的缝隙,应采用岩棉或矿模等材料填充,其厚度不应小于100mm
B.
防火层应采用厚度不小于1.2mm的镀锌钢板承托
C.
承托板与主体结构、幕墙结构及承托板之间的缝隙应采用防火密封胶密封
D.
同一幕墙玻璃单元不应跨越两个防火分区
E.
防火层可与幕墙玻璃直接接触,但防火材料朝玻璃面处应采用装饰材料覆盖
【多选题】窗的构造尺寸应包括预留洞口与待安装窗框的间隙及墙体饰面材料的厚度。下列间隙中符合的有()mm。
A.
清水墙10
B.
墙体外饰面抹水泥砂浆或贴马赛克15~20
C.
墙体外饰面贴釉面瓷砖5~10
D.
墙体外饰面贴釉面瓷砖20~25
E.
墙体外饰面贴大理石或花岗岩板40~50